When crystallizers are classified based on the mode of material circulation, the three most commonly used types are External Circulation Crystallizers (FC Crystallizer), DTB (Draft Tube Baffle) Crystallizers, and OSLO Crystallizers. Each of these types has distinct structural characteristics and operational principles tailored to different crystallization requirements. The following sections provide a detailed overview of their design features, working mechanisms, and typical industrial applications. This paper begins with an in-depth look at the External Circulation Crystallizer (FC Crystallizer).
External Circulation Crystallizer (FC Type)
The External Circulation Crystallizer (FC Type) is a widely used evaporative crystallization system known for its simple structure, high reliability, and efficient control over crystal quality. It is commonly applied in chemical and pharmaceutical industries for the production of inorganic salts like ammonium sulfate and sodium chloride.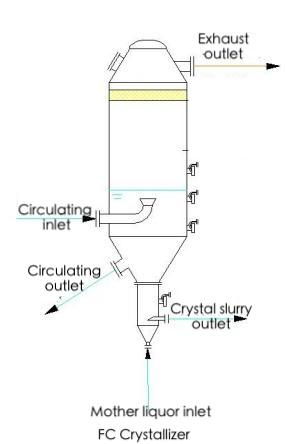
Structure and Working Principle
The FC crystallizer, also known as an externally heated forced circulation evaporative crystallizer, mainly consists of:
• A heating chamber(heat exchanger)
• An evaporative crystallization chamber
• Upper and lower circulation pipes
• A forced circulation pump
Working Cycle: Slurry is discharged from the conical bottom of the crystallization chamber and pumped by an axial-flow circulation pump through a heat exchanger (for heating or cooling), then returned to the crystallization chamber, forming a continuous external circulation loop. The resulting crystal size is relatively small, typically ranging from 0.15 to 0.3 mm.
Operational Features
• High circulation flow rate: helps maintain control over supersaturation and reduces secondary nucleation (which can result in overly fine crystals).
• Separated heat exchanger: simplifies cleaning and maintenance, particularly effective for scaling-prone or high-viscosity solutions.
Design Considerations
• The evaporative crystallization chamber should be positioned 4 to 6 meters higher than the heating chamber (from the crystallizer liquid level to the upper tube sheet of the heat exchanger). This prevents boiling at the upper inlet of the heat exchanger, avoiding crystal precipitation and tube blockage.
•Flow velocity:
Upper circulation pipe: < 1 m/s
Lower circulation pipe: 1.5–2.0 m/s
This setup accommodates vapor bubbles that may form in the upper pipe due to vacuum effects as the heated solution enters the crystallization chamber.
To prevent flash boiling, the upper pipe diameter should be slightly larger than the lower pipe. If vacuum levels are low, both pipes can be of equal diameter.
Application Scenarios
FC crystallizers are widely used in:
• Chemical and pharmaceutical manufacturing
• Production of crystals such as: Ammonium sulfate ((NH4)2SO4), Sodium chloride (NaCl) and etc.
Conclusion
The FC Type crystallizer is an effective and economical choice for medium-to-large scale crystallization processes. Its external circulation design offers excellent control over heat transfer, supersaturation, and crystal quality, making it a popular choice across multiple industries.
Enchem is here to listen to your needs and provide sustainable solutions. Contact us to discover more.Get In Touch With US

