What Is an Evaporator?
An evaporator is a device that heats a liquid to convert the solvent—typically water—into vapor. This process is used to concentrate the solution or to separate the solvent from solutes. Evaporators are widely applied in industries such as: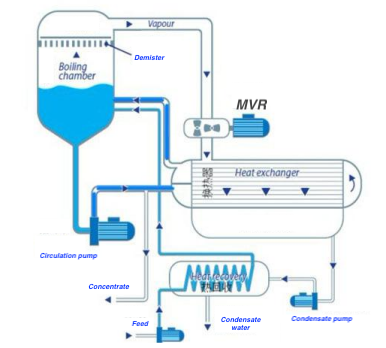
• Chemicals
• Pharmaceuticals
• Food processing
• Environmental protection
• Battery material production
In addition to achieving concentration and separation, ensuring the quality of the recovered condensate is critical—especially in applications where the condensate is reused or must meet stringent environmental regulations.
Key Measures to Ensure Condensate Quality
To maintain high condensate purity, several design and operational measures are commonly implemented in modern evaporator systems:
1. Demister System
A well-designed three-stage demister, combined with optimized vapor velocity and separation height, effectively reduces the risk of liquid droplet entrainment, protecting the quality of the condensate.
2. Evaporation Boiling Point Control
A Heat and Balance System (HABS) ensures precise temperature control during evaporation. This prevents high-boiling-point contaminants from vaporizing and entering the condensate stream.
3. pH Adjustment System
An automated acid/alkali dosing system adjusts the pH of the feed based on real-time COD and pH readings, ensuring stable water quality in the condensate.
4. Foam Detection and Antifoaming
A foam monitoring system detects abnormal foaming and automatically doses antifoaming agents to prevent foam-related contamination and carryover.
5. Upstream and Downstream Pretreatment Modules
Where needed, pretreatment and post-treatment systems—such as precipitation tanks, filtration units, oil-water separators, and reverse osmosis (RO)—are integrated to further purify the feed or polish the condensate.
6. Real-Time Instrumentation Monitoring
Online sensors installed at the condensate outlet provide continuous quality monitoring. If quality deviations occur, the system automatically recirculates or redirects non-compliant condensate for reprocessing.
Conclusion
The measures outlined above can be flexibly selected and applied based on the specific characteristics of the feed solution, the required condensate quality, and the overall system design. By tailoring these strategies to actual process conditions, the reliability and purity of the recovered condensate in various industrial evaporation applications can be ensured.
Get In Touch With US
Enchem is here to listen to your needs and provide sustainable solutions. Contact us to discover more.

