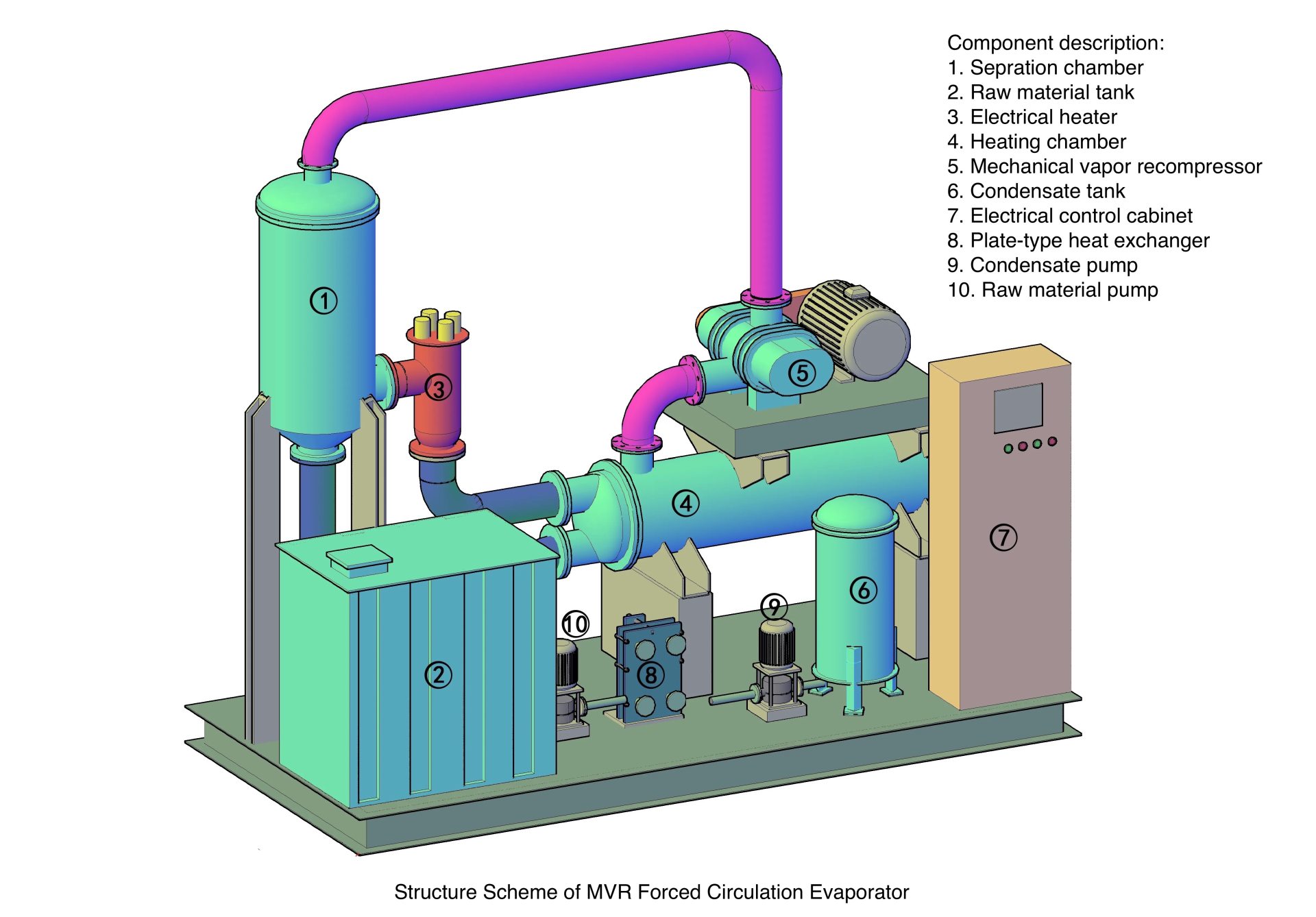
Technical background of MVR evaporator
Evaporation, distillation, evaporation-crystallization, and evaporation-drying systems are all known for their high energy consumption. Energy usage accounts for a significant portion of the operating costs for these types of equipment. Therefore, reducing and optimizing specific energy consumption is a critical strategy for lowering overall operational expenses.
To address this challenge, there are three main technologies commonly used to minimize energy consumption. These technologies can be implemented independently or combined, depending on process requirements:
• Multiple-Effect Evaporation (MEE)
This method reuses the vapor from one effect as the heating medium for the next, reducing steam consumption across multiple stages.
• Thermal Vapor Recompression (TVR)
TVR systems utilize steam ejectors to recompress a portion of the vapor, increasing its temperature and allowing it to be reused as a heat source.
• Mechanical Vapor Recompression (MVR)
MVR systems mechanically compress the secondary vapor generated during evaporation to elevate its temperature, pressure and enthalpy, enabling it to be reused as a heating medium in the heat exchanger for incoming feed material.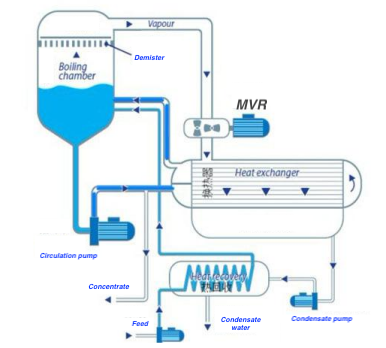
Among these technologies, MVR technology offer the lowest energy consumption, making them the most energy-efficient solution for many industrial applications. By leveraging mechanical energy rather than thermal input, MVR systems significantly reduce external steam demand and provide a more sustainable and cost-effective approach to evaporation.
MVR: A High-Efficiency, Energy-Saving Evaporation Technology
Mechanical Vapor Recompression (MVR technology) is an advanced energy-saving technology that recycles the energy from its own secondary steam, significantly reducing the need for external energy sources such as fresh steam.
In an MVR evaporator, the low-temperature secondary vapor generated during the evaporation process is compressed by a compressor. This compression increases the vapor’s temperature, pressure, and enthalpy, transforming it into a high-grade heating medium. The compressed vapor is then directed back into the evaporator’s heating chamber, where it provides the thermal energy required to keep the feed liquid boiling. During this process, the heating vapor condenses into condensate, and the previously discarded secondary steam is fully reused. This efficient recovery of latent heat greatly enhances thermal efficiency. In fact, the steam economy of an MVR evaporator is equivalent to that of a traditional 30-effect evaporator.
Applications of MVR Technology
MVR (Mechanical Vapor Recompression) technology is widely applied across various industries that require efficient and continuous evaporation. Thanks to its low energy consumption, compact design, and high thermal efficiency, MVR has become a preferred solution in both environmental and industrial processing fields.
• Chemical Industry
Concentration of chemical solutions such as sodium sulfate, ammonium chloride, and phosphoric acid
Recovery of solvents and valuable components
Crystallization of salts from brine or process liquors
• Pharmaceutical Industry
Concentration of pharmaceutical intermediates and APIs
Treatment of high-COD wastewater from drug production
Recovery of heat-sensitive compounds using low-temperature MVR systems
• Food and Beverage Industry
Concentration of juices, dairy products (e.g., whey, milk), and liquid sweeteners
Production of extracts and flavorings
• New Energy Materials
Concentration and purification processes in lithium carbonate, lithium hydroxide, and ternary precursor production
Treatment of lithium iron phosphate (LFP) and nickel-cobalt-manganese (NCM) production wastewater
• Metallurgical Industry
Evaporation and crystallization of metal salt solutions
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) applications in hydrometallurgy
Concentration of acidic or alkaline leachates
• Environmental Protection
High-salinity wastewater treatment from chemical and textile plants
Leachate treatment in solid waste management and landfills
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) systems to comply with environmental regulations
• Bio-Fermentation and Biotechnology
Concentration of fermentation broths
Recovery of organic acids, amino acids, and enzymes
Efficient handling of heat-sensitive biological liquids
• Solvent Recovery
MVR technology is also effectively applied in the recovery of organic solvents—such as ethanol, methanol, and isopropanol—used in extraction and purification processes across the chemical, pharmaceutical, and biotechnology industries.
Contact US
Enchem is here to listen to your needs and provide sustainable solutions. Contact us to discover more